.jpeg)
.jpeg)
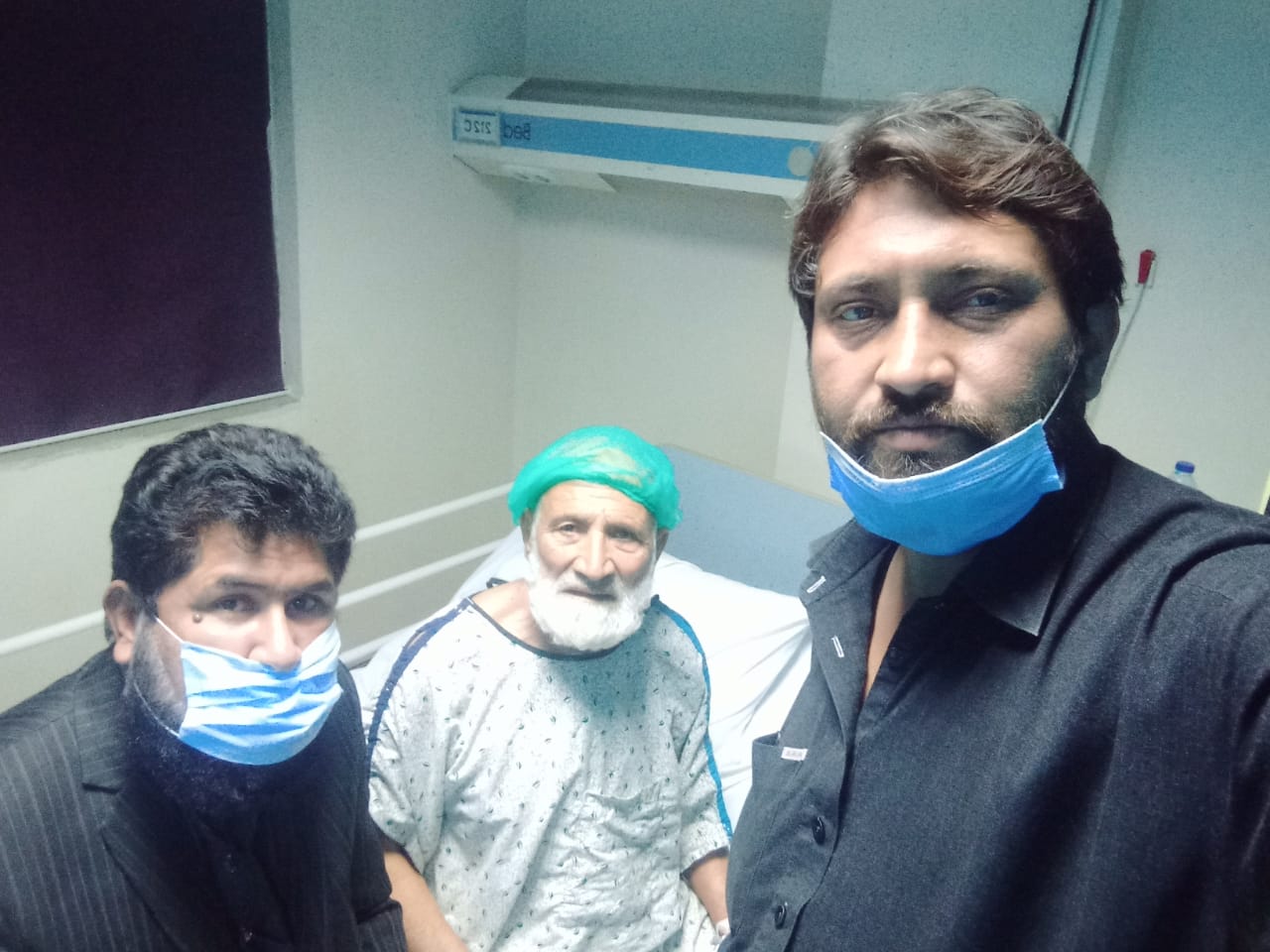

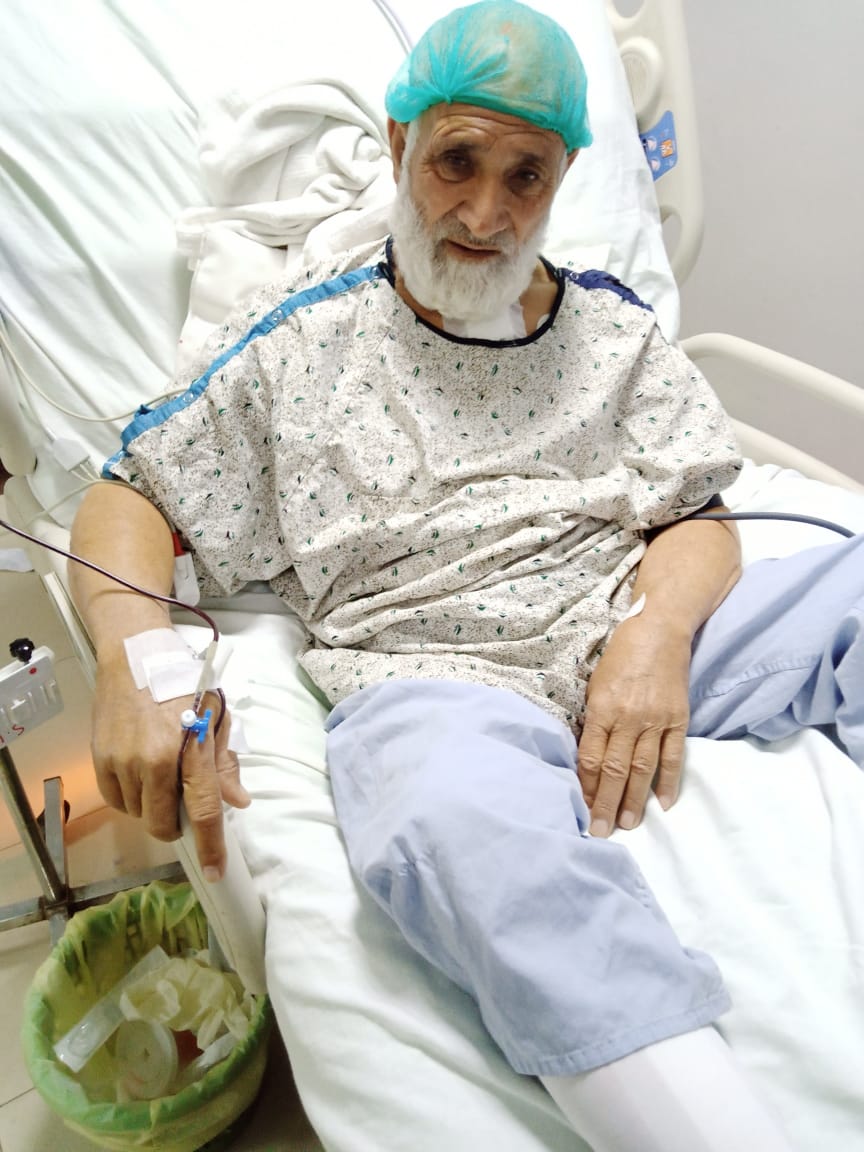
Open Heart Surgery (Valve Replacement Surgery)
A patient with severe aortic valve stenosis presents with shortness of breath, chest pain, and dizziness. Diagnostic tests, including echocardiogram and cardiac MRI, reveal significant narrowing of the aortic valve, causing obstructed blood flow and leading to heart dysfunction. Indication for Surgery: Valve replacement surgery is recommended to replace the damaged aortic valve with a mechanical or biological valve to restore normal blood flow, alleviate symptoms, and prevent further heart complications. Procedure: Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered. Incision: A median sternotomy is performed to access the heart. Valve Replacement: The diseased aortic valve is removed and replaced with either a mechanical or biological valve. Reperfusion: The heart is restarted, and normal blood flow is restored. Postoperative Care: The patient is monitored in the ICU for 24-48 hours, with pain management, monitoring for complications, and gradual mobilization. Complications and Recovery: Common complications include infection, bleeding, and potential valve dysfunction. The patient experiences mild postoperative bleeding, which is managed effectively. There are no major issues with the new valve, and the patient recovers with ongoing monitoring. Outcome: The surgery is successful, with significant improvement in symptoms, such as alleviation of shortness of breath and chest pain. The patient’s heart function improves, and follow-up evaluations show the new valve is functioning well. Conclusion: Valve replacement surgery is an effective treatment for patients with severe valve disease. By restoring proper heart function and alleviating symptoms, patients can experience improved quality of life. With proper postoperative care and regular follow-ups, patients can enjoy long-term recovery and heart health.


Comments
Post a Comment