.jpeg)
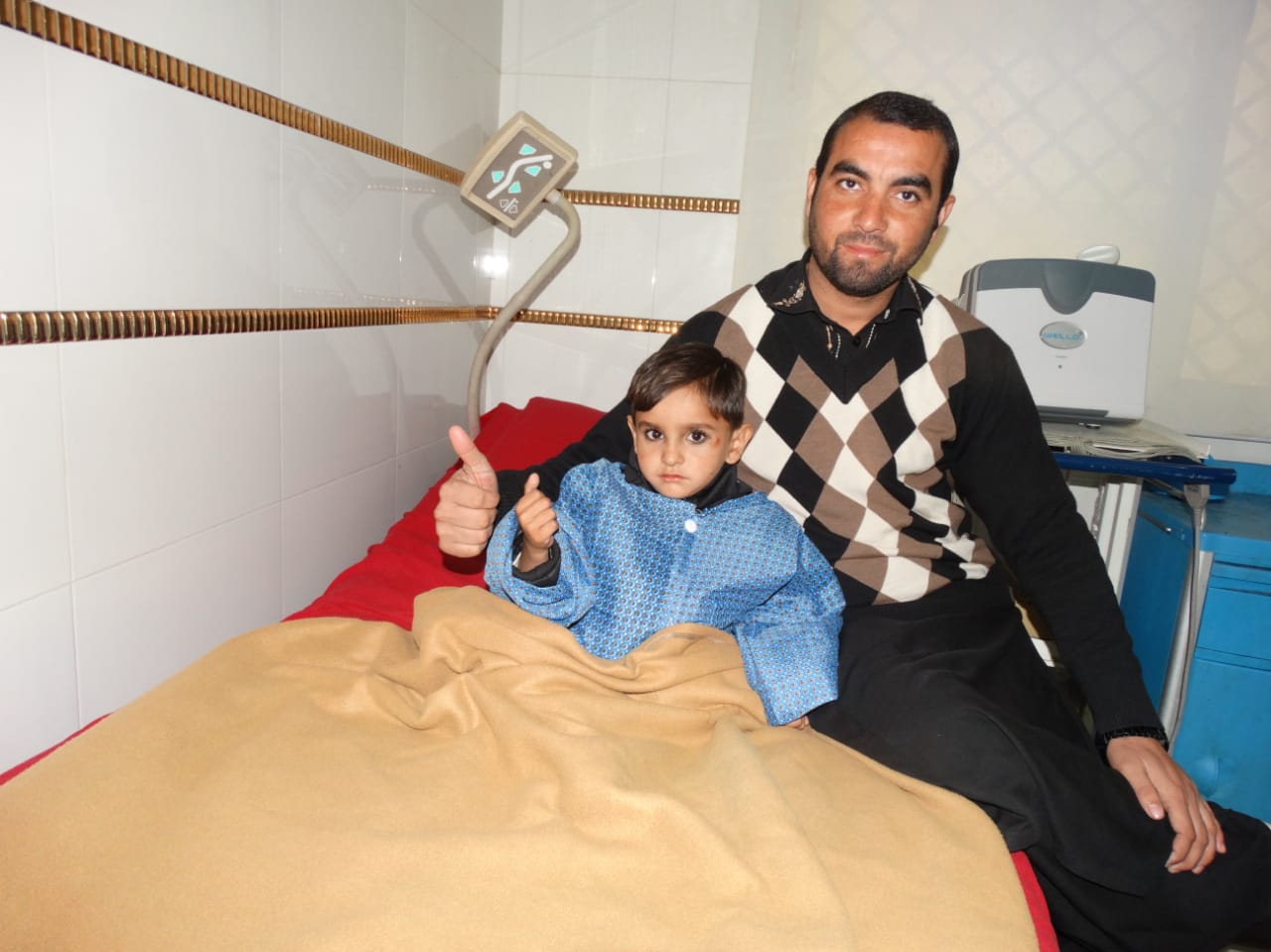
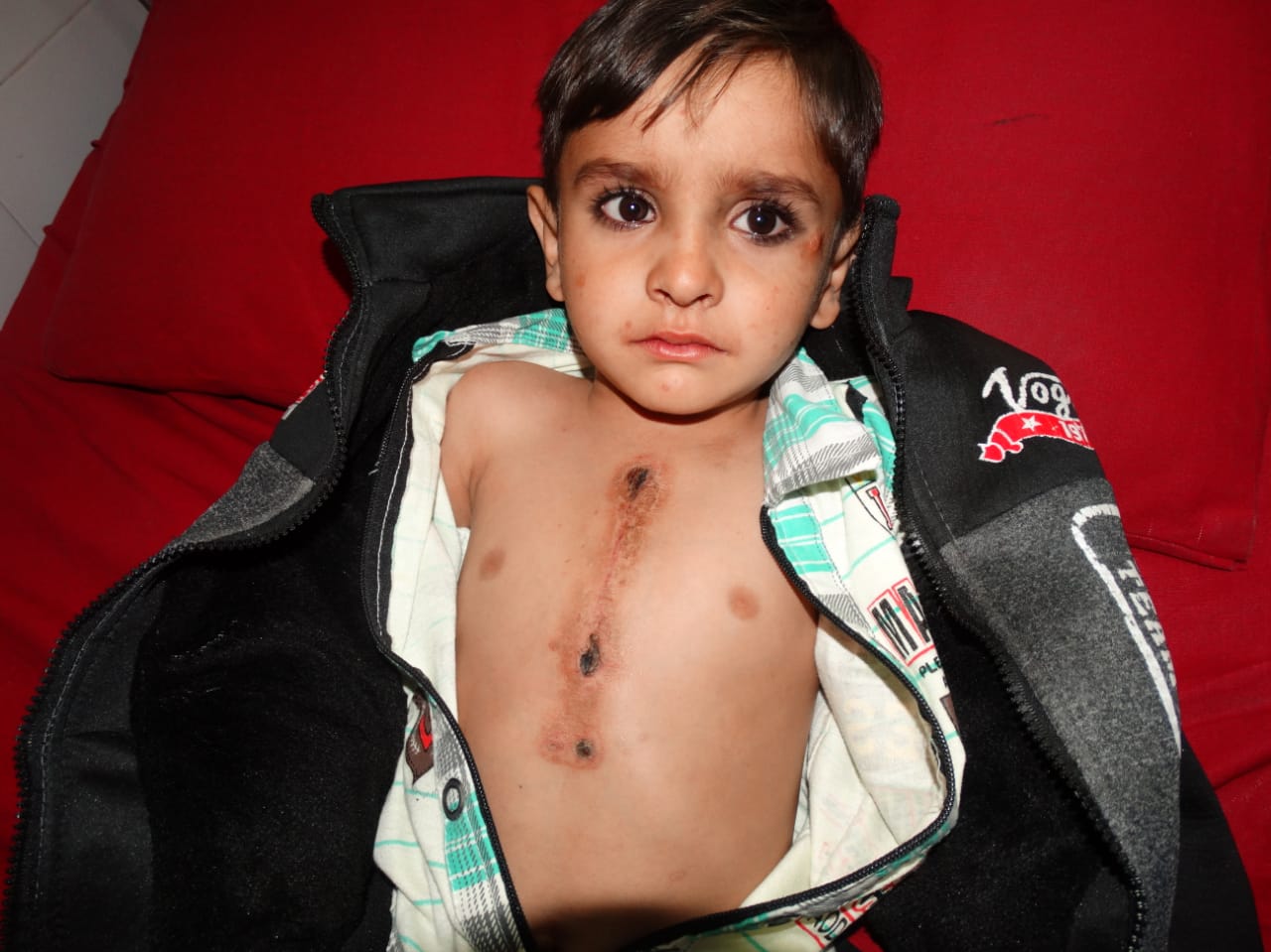
Open Heart Surgery (Ventricular Septal Defect - VSD Repair)
A patient, typically a child or adult with a congenital condition, presents with symptoms of heart failure, including fatigue, difficulty breathing, and poor weight gain in infants. Diagnostic tests, including echocardiogram and cardiac MRI, reveal a Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD), a hole in the wall (septum) that separates the left and right ventricles of the heart. This defect leads to abnormal blood flow between the two ventricles. Indication for Surgery: Surgery is recommended to repair the VSD, as the condition can lead to increased pressure in the lungs, heart failure, and other complications if left untreated. Repairing the hole restores normal blood flow and prevents further damage to the heart and lungs. Procedure: Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered. Incision: A median sternotomy is performed to access the heart. VSD Repair: The surgeon closes the hole in the ventricular septum, typically using a patch made of synthetic material or tissue from the patient (pericardium). Reperfusion: Blood flow is restored, and the heart is restarted. Postoperative Care: The patient is closely monitored in the ICU for 24-48 hours, with pain management, infection prevention, and gradual mobilization. Complications and Recovery: Possible complications include infection, bleeding, arrhythmias, or residual leakage from the repair site. In this case, the patient has mild postoperative bleeding and temporary arrhythmias, which are managed effectively. The patient’s recovery is generally uneventful, and heart function improves after the repair. Outcome: The surgery is successful, and the patient's symptoms, such as fatigue and difficulty breathing, improve significantly. Follow-up echocardiograms show no residual VSD, and the heart is functioning normally. Conclusion: Ventricular Septal Defect repair is a highly effective surgical treatment for patients with this congenital heart condition. It restores normal heart function, improves quality of life, and prevents long-term complications. Postoperative care, including regular follow-ups, is essential for monitoring the repair and ensuring long-term success.


Comments
Post a Comment