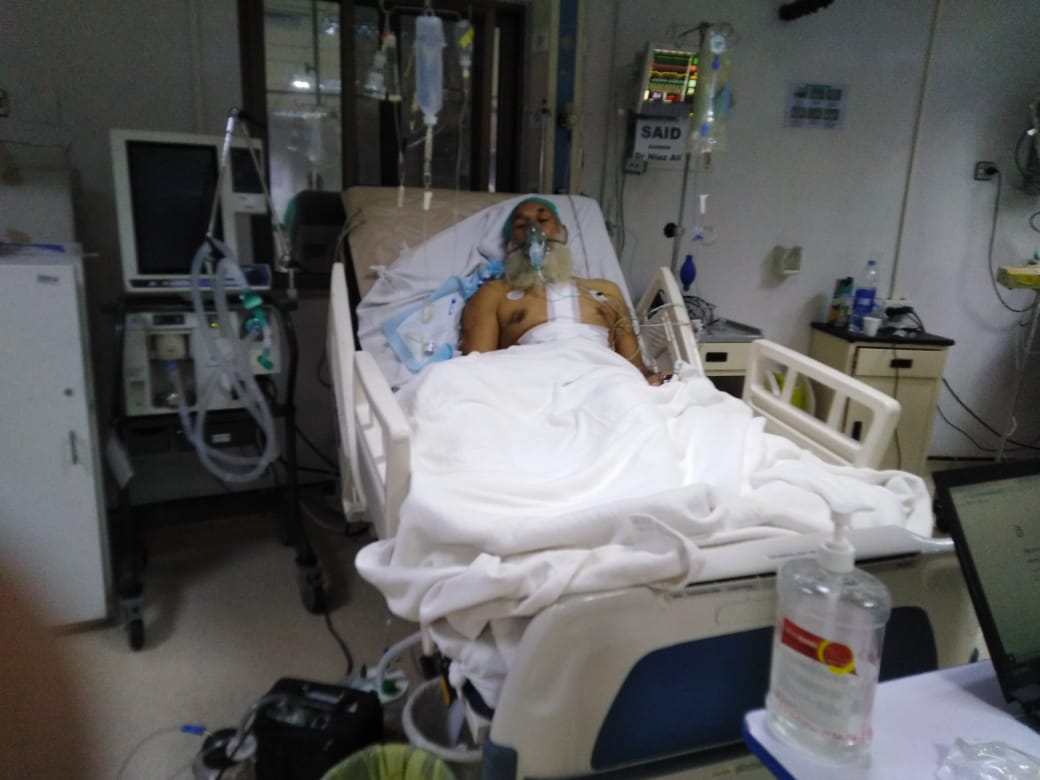
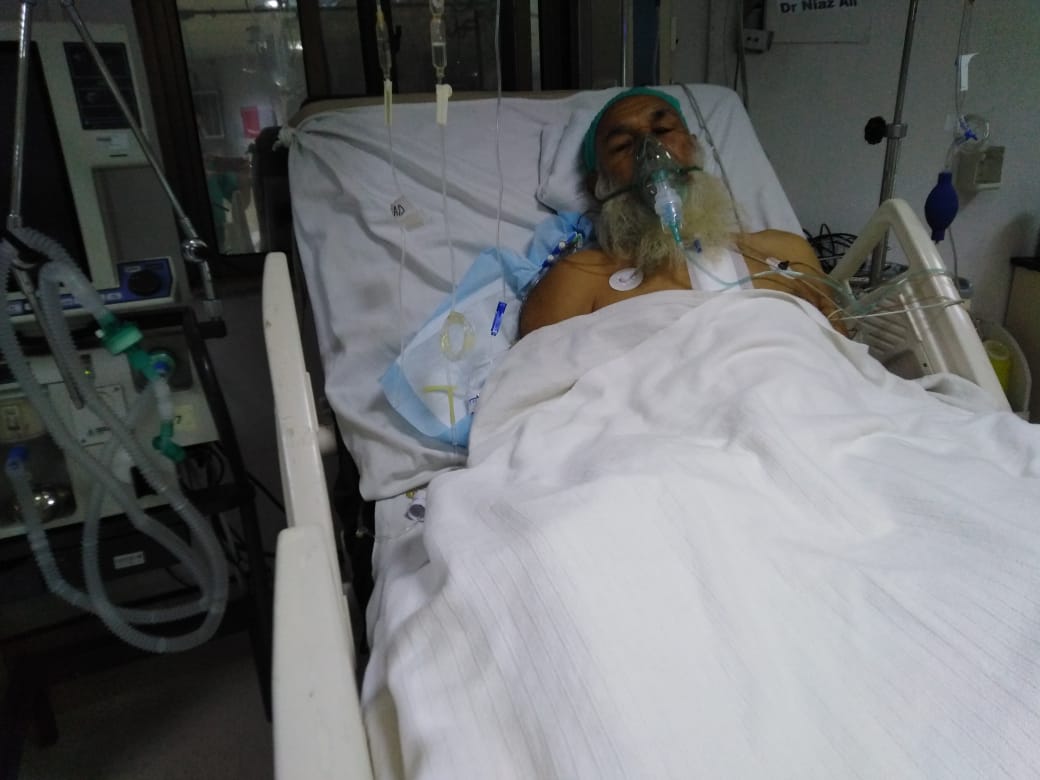
Open Heart Surgery (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting - CABG)
A patient with severe coronary artery disease (CAD) presents with chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Diagnostic tests reveal multiple blockages in the coronary arteries, including the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and right coronary artery (RCA), leading to a recommendation for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). Indication for Surgery: CABG is recommended to bypass the blocked arteries and restore proper blood flow to the heart, improving symptoms and preventing further heart damage. Procedure: Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered. Incision: A median sternotomy is performed to access the heart. Grafting: Healthy blood vessels are harvested from the patient's leg or chest and used to bypass the blocked coronary arteries. Reperfusion: Blood flow is restored, and the heart is restarted. Postoperative Care: The patient is monitored in the ICU for 24-48 hours, with pain management, monitoring for complications, and gradual mobilization. Complications and Recovery: Common complications include bleeding, infection, and arrhythmias, which are managed effectively. The patient experiences mild postoperative bleeding and temporary arrhythmias but recovers without major issues. Outcome: The surgery is successful, with significant improvement in the patient's symptoms and heart function. Postoperative rehabilitation, including lifestyle changes and regular follow-ups, ensures long-term health and prevents further complications. Conclusion: CABG is an effective procedure for treating severe CAD, significantly improving symptoms and heart function. With proper postoperative care and lifestyle changes, patients can experience enhanced quality of life and long-term recovery.


Comments
Post a Comment